Comparing
You can compare different Period objects according to their bounds, datepoints or durations.
Using durations
Sorting objects
public Period::durationCompare(Period $duration): int
public Period::durationGreaterThan(Period $duration): bool
public Period::durationLessThan(Period $duration): bool
public Period::durationEquals(Period $duration): bool
The method Period::durationCompare compares two Period objects according to their duration. The method returns:
1if the current object duration is greater than the submitted object duration;-1if the current object duration is lesser than the submitted object duration;0if the current object duration is equal to the submitted object duration;
To ease the method usage you can rely on the following proxy methods:
Period::durationGreaterThanreturnstruewhenPeriod::durationComparereturns1Period::durationLessThanreturnstruewhenPeriod::durationComparereturns-1Period::durationEqualsreturnstruewhenPeriod::durationComparereturns0
Examples
$orig = Period::after('2012-01-01', '1 MONTH');
$alt = Period::after('2012-01-01', '1 WEEK');
$other = Period::after('2013-01-01', '1 MONTH');
$orig->durationCompare($alt); //return 1
$orig->durationGreaterThan($alt); //return true
$orig->durationLessThan($alt); //return false
$alt->durationCompare($other); //return -1
$alt->durationLessThan($other); //return true
$alt->durationGreaterThan($other); //return false
$orig->durationCompare($other); //return 0
$orig->durationEquals($other); //return true
$orig->equals($other); //return false
//the duration between $orig and $other are equals but not the datepoints!!
Returning the duration differences
public Period::dateIntervalDiff(Period $period): DateInterval
public Period::timeDurationDiff(Period $period): int
Returns the duration difference between two Period objects using a DateInterval object or expressed in seconds.
Examples
use League\Period\Period;
$interval = Period::fromSemester(2012, 1);
$altInterval = Period::fromIsoWeek(2012, 4);
$diff = $interval->dateIntervalDiff($altInterval);
// $diff is a DateInterval object
$diffAsSeconds = $interval->timeDurationDiff($altInterval);
//$diffAsSeconds represents the interval expressed in seconds
Using datepoints and bounds
All following methods results take into account the interval datepoints as well as its boundary types.
Period::isBefore
public Period::isBefore(Period|DatePoint|DateTimeInterface|string $timeSlot): bool
Tells whether the current Period object datetime continuum is entirely before the specified $timeSlot.
Examples
$period = Period::fromMonth(1983, 4);
$alt = Period::fromMonth(1984, 4);
//test against another Period object
$period->isBefore($alt); //returns true;
$alt->isBefore($period); //return false;
//test againts a datepoint
$period->isBefore('1983-06-02'); //returns true
$period->isBefore('1982-06-02'); //returns false
$period->isBefore($period->getEndDate()); //returns true
Period::isDuring
public Period::isDuring(Period $timeSlot): bool
A Period is contained into another if its datetime continuum is completely contained within the submitted Period datetime continuum.
Examples
//comparing a datetime
$period = Period::fromMonth(1983, 4);
//comparing two Period objects
$alt = Period::after('1983-04-12', '12 DAYS');
$period->contains($alt); //return true;
$alt->isDuring($period); //return true;
Period::isAfter
public Period::isAfter(Period|DatePoint|DateTimeInterface|string $timeSlot): bool
Tells whether the current Period object datetime continuum is entirely after the specified $timeSlot.
Examples
$period = Period::fromMonth(1983, 4);
$alt = Period::fromMonth(1984, 4);
//test against another Period object
$alt->isAfter($period); //returns true;
$period->isAfter($alt); //return false;
//test againts a datepoint
$period->isAfter('1983-06-02'); //returns false
$period->isAfter('1982-06-02'); //returns true
$period->isAfter($period->startDate); //returns false
Period::bordersOnStart
public Period::bordersOnStart(Period $timeSlot): bool
A Period borders on the starting datepoint of another instance if its ending datepoint is immediately before the submitted Period starting datepoint without overlapping.
Examples
//comparing a datetime
$period = Period::fromMonth(1983, 4);
//comparing two Period objects
$alt = Period::fromMonth(1983, 3);
$alt->bordersOnStart($period); //return true;
Period::bordersOnEnd
public Period::bordersOnEnd(Period $timeSlot): bool
A Period borders on the ending datepoint of another instance if its starting datepoint is immediately after the submitted Period end datepoint without overlapping.
Examples
//comparing a datetime
$period = Period::fromMonth(1983, 4);
//comparing two Period objects
$alt = Period::fromMonth(1983, 3);
$period->bordersOnEnd($alt); //return true;
Period::abuts
public Period::abuts(Period $timeSlot): bool
A Period abuts if it starts immediately after, or ends immediately before the submitted Period without overlapping.
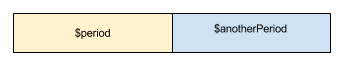
Examples
$period = Period::fromMonth(2014, 3);
$alt = Period::fromMonth(2014, 4);
$period->abuts($alt); //return true
//in this case $period->endDate == $alt->startDate;
Periods::meetsOnStart
public Period::meetsOnStart(Period $timeSlot): bool
A Period meets on the starting datepoint of another instance if its ending datepoint equals the submitted Period starting datepoint and
theirs respective bounds are inclusive.
Example
use League\Period\Bounds;
use League\Period\Period;
$period = Period::fromMonth(2014, 3, Bounds::IncludeAll);
$alt = Period::fromMonth(2014, 4, Bounds::IncludeStartExcludeEnd);
$period->meetsOnStart($alt); //return true
//in this case
// $period->endDate == $alt->startDate
// $period->bounds->isEndIncluded() returns true
// $alt->bounds->isStartIncluded() returns true
Periods::meetsOnEnd
public Period::meetsOnEnd(Period $timeSlot): bool
A Period meets on the ending datepoint of another instance if its start datepoint equals the submitted Period ending datepoint and
theirs respective bounds are inclusive.
Examples
use League\Period\Bounds;
use League\Period\Period;
$period = Period::fromDate('2022-02-01', '2022-03-01', Bounds::IncludeStartExcludeEnd),
$alt = Period::fromDate('2022-01-01', '2022-02-01', Bounds::ExcludeStartIncludeEnd),
$period->meetsOnEnd($period); //return true
//in this case
// $period->startDate == $alt->endDate;
// $period->bounds->isStartIncluded() returns true
// $alt->bounds->isEndIncluded() returns true
Periods::meets
public Period::meets(Period $timeSlot): bool
A Period meets on the ending datepoint or on the starting datepoint of another instance and their bounds
are incluse when they meet. This method returns true if both period returns true on meetsOnStart or meetsOnEnd.
Examples
use League\Period\Bounds;
use League\Period\Period;
$period = Period::fromDate('2022-02-01', '2022-03-01', Bounds::IncludeStartExcludeEnd),
$alt = Period::fromDate('2022-01-01', '2022-02-01', Bounds::ExcludeStartIncludeEnd),
$period->meets($period); //return true
Period::overlaps
public Period::overlaps(Period $timeSlot): bool
A Period overlaps another if they share some common part of their respective continuous portion of time without abutting.
Examples
$orig = Period::fromMonth('2014-03-15');
$alt = Period::fromMonth('2014-04-15');
$other = Period::after('2014-03-15', '3 WEEKS');
$orig->overlaps($alt); //return false
$orig->overlaps($other); //return true
$alt->overlaps($other); //return true
Period::isStartedBy
public Period::isStartedBy(Period|DatePoint|DateTimeInterface|string $timeSlot): bool
- Tells whether both
Periodobjects starts at the same datepoint. - Tells whether the submitted
DateTimeInterfaceobject is the interval included starting datepoint
Examples
$period = Period::fromMonth(2014, 3);
$alt = Period::after('2014-03-01', '2 DAYS');
$period->isStartedBy($alt); //return true
//in this case $period->startDate == $alt->startDate;
// and $period->isStartIncluded === $alt->isStartIncluded;
Period::isEndedBy
public Period::isEndedBy(Period|DatePoint|DateTimeInterface|string $timeSlot): bool
- Tells whether both
Periodobjects ends at the same datepoint. - Tells whether the submitted
DateTimeInterfaceobject is the interval included ending datepoint
Examples
$period = Period::fromMonth(2014, 3);
$alt = Period::before('2014-04-01', '2 DAYS');
$period->isEndedBy($alt); //return true
//in this case $period->getEndDate() == $alt->getEndDate();
// and $period->isEndExcluded() === $alt->isEndExcluded();
Period::equals
public Period::equals(Period $timeSlot): bool
Tells whether two Period objects shares the same datepoints and the same boundary type.
Examples
$orig = Period::fromMonth(2014, 3);
$alt = Period::fromMonth(2014, 4);
$other = Period::after('2014-03-01', '1 MONTH');
$otherInclusif = Period::after('2014-03-01', '1 MONTH', Period::INCLUDE_ALL);
$orig->equals($alt); //return false
$orig->equals($other); //return true
$orig->equals($otherInclusif); //return false because the boundary are not the same
Period::contains
public Period::contains(Period|DatePoint|DateTimeInterface|string $timeSlot): bool
- A
Periodcontains a datepoint reference if this datepoint is present in its datetime continuum. - A
Periodcontains anotherPeriodobject if the latter datetime continuum is completely contained within thePerioddatetime continuum.
Examples
//comparing a datetime
$period = Period::fromMonth(1983, 4);
$period->contains('1983-04-15'); //returns true;
$period->contains($period->startDate); //returns true;
$period->contains($period->endDate); //returns false;
//comparing two Period objects
$alt = Period::after('1983-04-12', '12 DAYS');
$period->contains($alt); //return true;
$alt->contains($period); //return false;
Period::gap
public function gap(Period $period): Period
A Period has a gap with another Period if there is a non-zero interval between them. This method returns the amount of the gap as a new Period object only if they do actually have a gap between them. If they overlap a IntervalError is thrown.

Examples
$interval = Period::after('2012-01-01', '2 MONTHS');
$altInterval = Period::after('2013-01-15', '3 MONTHS');
$gap = $interval->gap($altInterval);
Period::intersect
public function intersect(Period ...$periods): Period
An Period overlaps another if it shares some common part of the datetime continuum. This method returns the amount of the overlap as a Period object, only if they actually do overlap. If they do not overlap, then an Period\IntervalError is thrown.
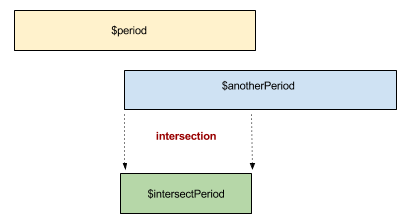
Examples
$interval = Period::after('2012-01-01', '2 MONTHS');
$altInterval = Period::after('2012-01-15', '3 MONTHS');
$intersection = $interval->intersect($altInterval);
Period::diff
public Period::diff(Period $interval): Sequence
This method returns the difference between two Period objects only if they actually do overlap. If they do not overlap or abut, then an IntervalError is thrown.
The difference is expressed as a Sequence instance. The object will:
- contains no
Periodobject if both interval share the same datepoints; - contains one
Periodobject if both objects share only one datepoint; - contains two
Periodobjects if no datepoint are shared between objects. The firstPerioddatetime continuum is always entirely set before the second one;
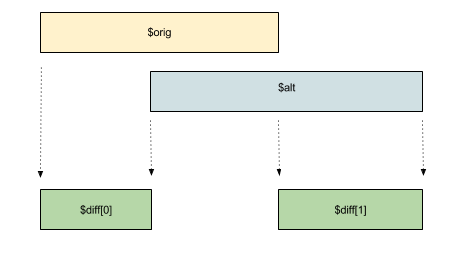
Examples
$orig = Period::after('2013-01-01', '1 MONTH');
$alt = Period::after('2013-01-15', '7 DAYS');
$sequence = $orig->diff($alt);
// $diff is an Sequence object containing 2 Period objects
$sequence[0]->equals(new Period('2013-01-01', '2013-01-15')); // returns true
$sequence[1]->equals(new Period('2013-01-23', '2013-02-01')); // returns true
$sequence[0]->isBefore($sequence[1]); //return true;
//this is always true when two Period objects are present
Period::subtract
public Period::subtract(Period ...$periods): Sequence
This method returns the difference between two or more Period objects. It differs from Period::diff as:
- the method is not commutative;
- the method never throws even when the instances do not overlaps;
Examples
$periodA = Period::after('2000-01-01 10:00:00', '8 HOURS');
$periodB = Period::after('2000-01-01 14:00:00', '6 HOURS');
$periodC = Period::before('2019-01-03', '1 MONTH');
$sequenceAB = $periodA->subtract($periodB);
count($sequenceAB); //returns 1
$sequenceAB[0]->equals
new Period($periodA->startDate, $periodB->startDate)
);
$sequenceBA = $periodB->subtract($periodA);
count($sequenceBA); //returns 1
$sequenceBA[0]->equals(
new Period($periodA->getEndDate(), $periodB->getEndDate())
);
$sequenceAC = $periodA->subtract($periodC);
count($sequenceAC); //returns 1
$sequenceAC[0]->equals($periodA); //returns true
$sequenceCA = $periodC->subtract($periodA);
count($sequenceCA); //returns 1
$sequenceCA[0]->equals($periodC); //returns true
Period::union
public Period::union(Period ...$periods): Sequence
This method returns the union between two Period objects.
Examples
$periodA = Period::after('2000-01-01 10:00:00', '8 HOURS');
$periodB = Period::after('2000-01-01 14:00:00', '6 HOURS');
$periodC = Period::before('2019-01-03', '1 MONTH');
$sequenceAB = $periodA->union($periodB);
count($sequenceAB); //returns 1
$sequenceBA = $periodB->union($periodA);
count($sequenceBA); //returns 1
$sequenceBA == $sequenceAB;
$sequenceAC = $periodA->subtract($periodC);
count($sequenceAC); //returns 1
$sequenceAC[0]->equals($periodA); //returns true
$sequenceCA = $periodC->union($periodA);
count($sequenceCA); //returns 2
$sequenceAC = $periodA->union($periodC);
count($sequenceAC); //returns 2
$sequenceCA == new Sequence($periodC, $periodA);
$sequenceCA == $sequenceAC;
